How to Invest in ETFs: A Beginner’s Guide for 2025

Investing in Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) is a strategic way for beginners to diversify their portfolio; this step-by-step guide simplifies the process for 2025, covering everything from understanding ETFs to choosing the right ones and managing your investments effectively.
Ready to dive into the world of ETF investing? This comprehensive guide, “How to Invest in ETFs: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners in 2025,” breaks down the process into simple, actionable steps, ensuring you’re well-equipped to make informed investment decisions.
Understanding ETFs: A Primer for New Investors
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) have become increasingly popular, especially among beginner investors. But what exactly are they, and why should you consider adding them to your portfolio? This section provides a fundamental overview of ETFs, explaining their structure, benefits, and how they differ from other investment vehicles.
What is an ETF?
An ETF is a type of investment fund that holds a collection of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities. It trades on stock exchanges, similar to individual stocks. ETFs offer diversification, allowing you to invest in a broad market segment or a specific industry with a single purchase.
Benefits of Investing in ETFs
ETFs come with several advantages. They typically have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds, making them a cost-effective investment option. Also, their diversification helps in mitigating risk, and their tradability provides flexibility in managing your portfolio.
- Diversification: Spread your investment across multiple assets.
- Low Cost: Lower expense ratios compared to many mutual funds.
- Trading Flexibility: Buy and sell ETFs like stocks throughout the trading day.
- Transparency: ETF holdings are usually disclosed daily, providing insight into where your money is invested.
In summary, ETFs are a great entry point into investing due to their low cost, diversification benefits, and ease of trading, making them an appealing option for beginners.
Setting Your Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance
Before investing in any asset, including ETFs, it’s crucial to define your financial goals and understand your risk tolerance. This will guide your investment choices and help you build a portfolio that aligns with your objectives and comfort level. Let’s explore how to set these crucial parameters.
Defining Your Investment Goals
Are you saving for retirement, a down payment on a house, or your children’s education? Clearly defining your investment goals will help you determine the time horizon and the amount you need to invest. Different goals may require different types of ETFs.
Assessing Your Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance refers to your ability to withstand potential losses in your investments. Are you comfortable with high-risk, high-reward investments, or do you prefer a more conservative approach? Your risk tolerance will influence the types of ETFs you choose.
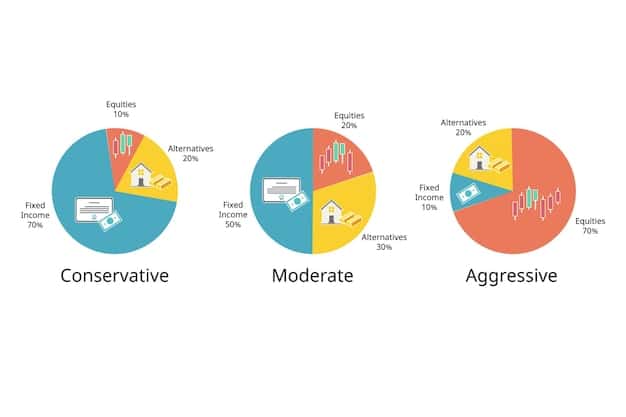
- Consider Your Age: Younger investors often have a longer time horizon and can afford to take on more risk.
- Evaluate Your Financial Situation: Assess your income, expenses, and savings.
- Think About Market Volatility: How would you react if your investments lost value?
Understanding your goals and risk tolerance will help you select ETFs that match your financial situation, ensuring a more aligned path toward achieving your investment objectives.
Opening a Brokerage Account: Your Gateway to ETFs
To start investing in ETFs, you’ll need to open a brokerage account. The process is straightforward. A good brokerage account is essential for accessing ETFs and managing your investments effectively. Selecting the right brokerage involves considering costs, tools, and services offered.
Choosing the Right Brokerage
There are many online brokerages to choose from, each with its own set of features and fees. Consider factors such as commission fees, account minimums, research tools, and customer support when making your decision.
Types of Brokerage Accounts
You can open different types of brokerage accounts, including individual retirement accounts (IRAs), taxable brokerage accounts, and custodial accounts for minors. The type of account you choose will depend on your financial goals and tax situation.
- Research Brokerage Options: Compare fees, tools, and account types.
- Consider Commission-Free Trading: Many brokerages now offer commission-free ETF trading.
- Evaluate Research Tools: Look for brokerages that provide helpful research and analysis.
Opening a brokerage account is your first step to accessing the ETF market, so choosing the right brokerage can significantly impact your investing journey.
Researching and Selecting ETFs: What to Look For
With thousands of ETFs available, knowing how to research and select the right ones is crucial. Not all ETFs are created equal. It’s essential to perform thorough research to identify ETFs that align with your investment goals and risk tolerance. This guide will help you navigate the ETF landscape.
Key Metrics to Consider
When evaluating ETFs, pay attention to key metrics such as the expense ratio, trading volume, assets under management (AUM), and tracking error. These metrics provide insights into the ETF’s cost, liquidity, size, and performance.
Types of ETFs
ETFs come in various types, including broad market ETFs, sector ETFs, bond ETFs, and international ETFs. Understanding the differences between these ETFs is essential for building a diversified portfolio that matches your goals.

- Check the Expense Ratio: Lower expense ratios mean more of your investment returns go to you.
- Evaluate Trading Volume: Higher trading volume usually means tighter bid-ask spreads.
- Understand the ETF’s Strategy: Know what the ETF is investing in and why.
- Diversify Your ETF Holdings: Avoid over-concentration in a single sector or asset class.
By carefully researching and selecting ETFs, you can make informed investment decisions that align with your financial objectives and risk tolerance.
Building a Diversified ETF Portfolio
Diversification is key to managing risk and achieving long-term investment success. A well-diversified portfolio includes a mix of asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions. This section guides you on how to construct a diversified ETF portfolio tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Asset Allocation Strategies
Begin by determining your ideal asset allocation, which is the percentage of your portfolio allocated to different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. Your asset allocation should align with your risk tolerance and time horizon.
Balancing Your Portfolio
Periodically review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation. Rebalancing involves selling some holdings and buying others to bring your portfolio back into alignment with your original plan.
- Consider Target-Date Funds: These funds automatically adjust their asset allocation over time, becoming more conservative as you approach retirement.
- Use a Strategic Mix of ETFs: Combine broad market ETFs, sector ETFs, and bond ETFs for diversification.
- Rebalance Regularly: At least annually, or more frequently if your portfolio deviates significantly from your target allocation.
By constructing a diversified ETF portfolio and rebalancing it regularly, you can reduce risk, capture opportunities, and stay on track toward achieving your financial goals.
Managing Your ETF Investments Over Time
Investing in ETFs isn’t a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process. Effective management involves continuous monitoring, periodic rebalancing, and staying informed about market conditions. Let’s explore the strategies of managing your ETF investments for long-term success.
Monitoring performance
Regularly review the performance of your ETFs to ensure they’re meeting your expectations. You can track performance through your brokerage account or use online portfolio tracking tools. Identify where adjustments are needed.
Staying Informed
Keep up-to-date with market news and economic trends that could impact your ETF investments. Being well-informed will help you make timely decisions and adjust your strategy as needed. Stay current in the financial landscape.
- Set Performance Benchmarks: Compare your ETFs’ performance against relevant market indices.
- Adjust Your Strategy as Needed: Life changes or market shifts may require adjustments to your portfolio.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a financial advisor if you need personalized guidance.
By proactively managing your ETF investments, you can enhance your returns, mitigate risks, and achieve your financial goals over the long term.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🎯 Define Goals | Set clear financial objectives to guide investment choices. |
| ⚖️ Assess Risk | Understand your comfort level with potential investment losses. |
| 💼 Open Account | Choose a brokerage that fits your needs and start investing. |
| 🔍 Research ETFs | Evaluate metrics like expense ratio and trading volume. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
▼
The expense ratio is the annual fee charged by an ETF to cover its operating expenses. It’s important because it directly impacts your returns; lower expense ratios result in higher net returns over time.
▼
Rebalance your portfolio at least annually or when your asset allocation deviates significantly from your target. This ensures that your portfolio remains aligned with your risk tolerance and financial goals.
▼
ETFs are generally tax-efficient due to their structure, but they can still generate capital gains or dividend income that is taxable. Consult a tax professional for personalized advice based on your situation.
▼
A sector ETF invests in companies within a specific industry or sector, such as technology, healthcare, or energy. They allow you to target specific areas of the market that you believe will outperform.
▼
You can find detailed information on the ETF provider’s website, financial news sites, and brokerage platforms. This data includes performance metrics, holdings, expense ratios, and other key details.
Conclusion
Investing in ETFs is an accessible and effective way for beginners to build a diversified portfolio and work towards their financial goals. By following these step-by-step guidelines, you can navigate the ETF market with confidence and make informed investment decisions that set you up for long-term success. From understanding the basics to managing your investments over time, you’re now equipped to start your ETF investing journey in 2025.



